Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
While selecting a suction strainer, the micron rating becomes one of the most important design decisions. Too coarse, and damaging particles enter the pump. Too fine, and the pump may starve due to flow restriction. The key is balance.
Hydraulic power packs rely on smooth, unrestricted oil flow to keep pumps healthy and systems reliable. Contaminants like dirt, fibers, or metal shavings can quickly damage pumps if left unchecked. That’s why suction strainers are installed at the pump inlet.
What Does Micron Rating Mean?
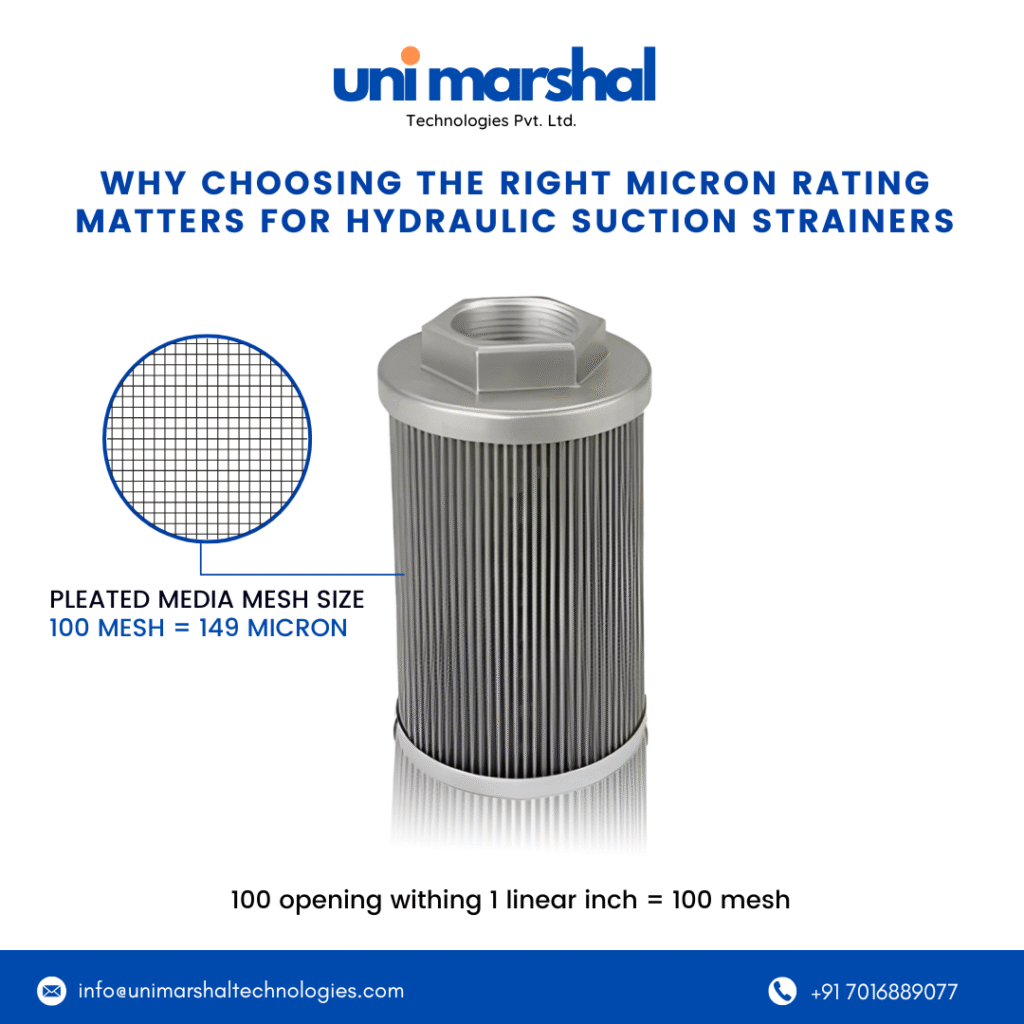
The micron rating refers to the particle size the strainer can capture.
- Example: A 125-micron strainer will trap particles ≥125 µm and let smaller particles pass.
Since suction strainers are the first line of defense, they are intentionally coarser than return or pressure filters, which capture much finer particles.
Why Micron Rating Selection is Critical
- Pump Protection
Correct micron rating ensures large debris like welding slag, fibers, or casting sand never reach the pump’s gears, vanes, or pistons. - Avoiding Cavitation
A strainer that is too fine will restrict oil flow, causing cavitation, noise, heat, and eventual pump failure. - System Reliability
By stopping large particles early, suction strainers reduce stress on downstream filters and components, extending system life.
Recommended Micron Ratings for Suction Strainers
Industry best practices (including OEM guidelines and engineering references) suggest:
- Typical Range: 74–250 microns (200 mesh and coarser) for suction strainers.
- Gear & Vane Pumps: ~125–200 µm (good balance of protection and flow).
- Piston Pumps (sensitive designs): 74–125 µm if OEM allows, but only with adequate open area to avoid cavitation.
- Harsh or Dusty Environments: 200–250 µm to prevent clogging and oil starvation.
👉 Important: Always follow your pump manufacturer’s recommendations, as pump tolerances and fluid conditions vary.
Checklist for Selecting the Right Suction Strainer
(Adapted from Power & Motion’s filter sizing guide, applied to suction strainers)
| Factor | Why It Matters | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Determines strainer size; too small restricts suction | Strainer open area ≥2–4× suction pipe area |
| Pipe Size | Prevents high velocity and turbulence | Match strainer to suction line diameter |
| Micron Rating | Balance between protection and flow | 74–250 µm typical |
| Fluid Viscosity | Thick or cold oil increases restriction | Use coarser mesh or larger basket |
| Pump Type | Sensitivity varies by design | Gear/Vane = 125–200 µm; Piston = finer if OEM allows |
| Material Compatibility | Prevent corrosion or fluid attack | Use SS304/316 for industrial fluids |
| Operating Conditions | Dirty or outdoor use demands robust design | Plan inspection and cleaning schedules |
Practical Tips for End Users
- Never use suction strainers finer than ~74 µm unless specified by OEM.
- Inspect and clean strainers regularly — clogged strainers starve pumps.
- Pair suction strainers with return or pressure filters (10–25 µm) for complete fluid cleanliness.
- Size for surface area, not just micron — bigger baskets reduce clogging risk.
Conclusion
Choosing the right micron rating for hydraulic suction strainers is not a small detail — it’s a critical safeguard for pump health and system efficiency. The ideal rating balances contaminant capture with unrestricted flow, ensuring reliability in hydraulic power packs across industries.
At Unimarshal Technologies, we manufacture suction strainers in multiple micron ratings and designs, tailored for power pack applications in India, UK, Africa, Japan, Russia, and Australia.
What is the function of a hydraulic suction strainer?
A suction strainer protects the hydraulic pump by capturing large contaminants before they enter the system.
What micron rating is recommended for suction strainers?
Most suction strainers range between 74–250 µm, depending on pump type, fluid viscosity, and application.
Can using too fine a suction strainer cause pump damage?
Yes. Very fine strainers can restrict oil flow, leading to pump cavitation, overheating, and premature failure.
How often should suction strainers be serviced?
They should be inspected and cleaned during regular maintenance or oil change cycles to avoid clogging.
Do suction strainers eliminate the need for return line or pressure filters?
No. Suction strainers only trap large debris. For full system cleanliness, they must be paired with finer return or pressure filters.